The RondoDox botnet malware is now exploiting a critical remote code execution (RCE) flaw in XWiki Platform tracked as CVE-2025-24893.
On October 30, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Information Security Agency (CISA) marked the flaw as actively exploited.
Now, a report from vulnerability intelligence company VulnCheck notes that CVE-2025-24893 is being leveraged in attacks by multiple threat actors, including botnet operators like RondoDox and cryptocurrency miners.
RondoDox is a large-scale botnet malware first documented by Fortinet in July 2025 as an emerging threat. In early October, Trend Micro warned about RondoDox’s exponential growth, with recent variants targeting at least 30 devices via 56 known vulnerabilities, some of them disclosed at Pwn2Own hacking competitions.
Starting November 3, VulnCheck observed RondoDox exploiting CVE-2025-24893 through a specially crafted HTTP GET request that injected base64-encoded Groovy code through the XWiki SolrSearch endpoint, causing the server to download and execute a remote shell payload.
The downloaded script (rondo.<value>.sh) is a first-stage downloader that retrieves and executes the main RondoDox payload.
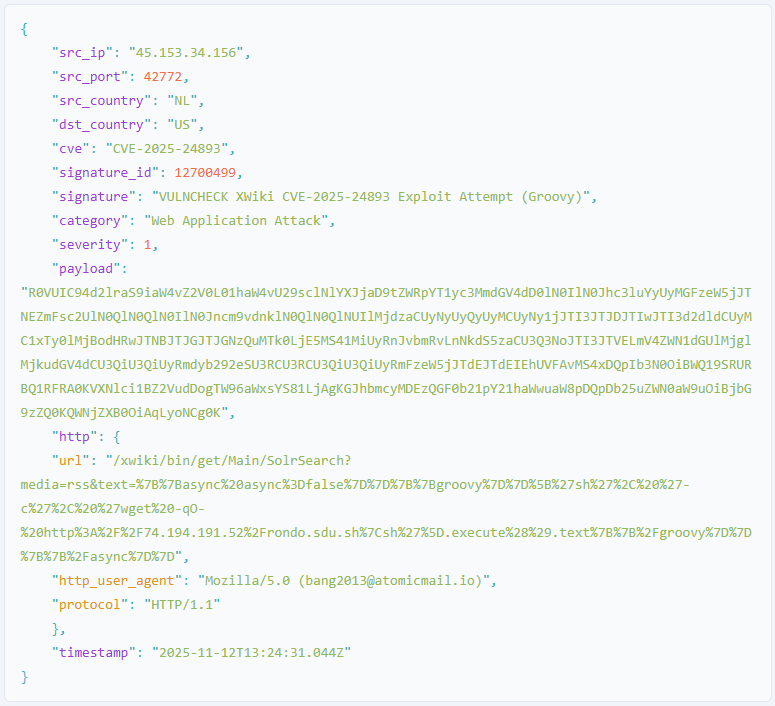
Source: VulnCheck
The researchers observed additional attacks involving cryptocurrency miner deployments on November 7, and also attempts to establish a bash reverse shell occurred on October 31 and November 11.
VulnCheck has also recorded widespread scanning using Nuclei, sending payloads that attempt to execute cat /etc/passwd via Groovy injection in the XWiki SolrSearch endpoint, as well as OAST-based probing.
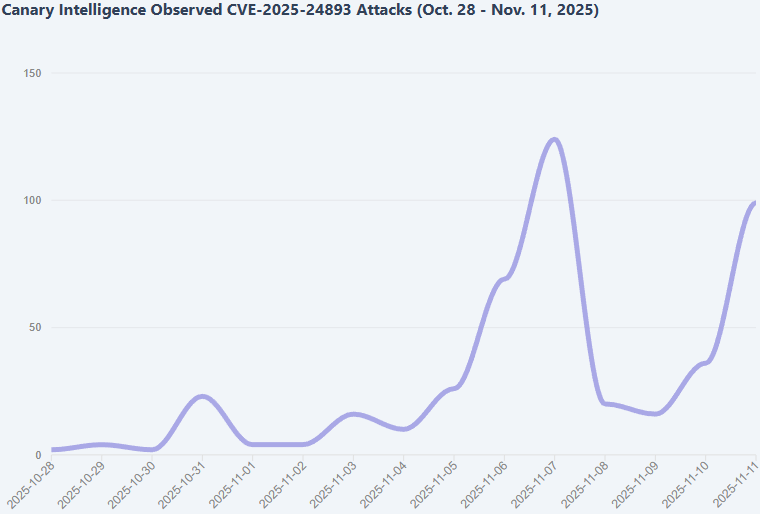
Source: VulnCheck
The XWiki Platform is a Java-based, open-source enterprise wiki platform used primarily for self-hosted internal knowledge management solutions.
CVE-2025-24893 impacts versions before 15.10.11 and 16.4.1, which are the upgrade targets for administrators. Given the active exploitation status for this flaw, immediate patching is advised.
According to the researchers, multiple attackers started to leverage the vulnerability just days after initial exploitation started.
They note that the incidents they observed come from a user-agent and documented payload servers associated with RondoDox. This means that publicly available indicators of compromise (IoCs) for the botnet should block these exploitation attempts.
Break down IAM silos like Bitpanda, KnowBe4, and PathAI
Broken IAM isn't just an IT problem - the impact ripples across your whole business.
This practical guide covers why traditional IAM practices fail to keep up with modern demands, examples of what "good" IAM looks like, and a simple checklist for building a scalable strategy.








Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now