
Over 3.6 million MySQL servers are publicly exposed on the Internet and responding to queries, making them an attractive target to hackers and extortionists.
Of these accessible MySQL servers, 2.3 million are connected over IPv4, with 1.3 million devices over IPv6.
While it is common for web services and applications to connect to remote databases, these instances should be locked down so only authorized devices can connect to them.
Furthermore, public server exposure should always be accompanied by strict user policies, changing the default access port (3306), enabling binary logging, monitoring all queries closely, and enforcing encryption.
3.6 million exposed MySQL servers
In scans performed last week by cybersecurity research group The Shadowserver Foundation, analysts found 3.6 million exposed MySQL servers using the default port, TCP port 3306.
"While we do not check for the level of access possible or exposure of specific databases, this kind of exposure is a potential attack surface that should be closed," explains the report from Shadow Server.
The country with the most accessible MySQL servers is the United States, surpassing 1.2 million. Other countries with substantial numbers are China, Germany, Singapore, the Netherlands, and Poland.
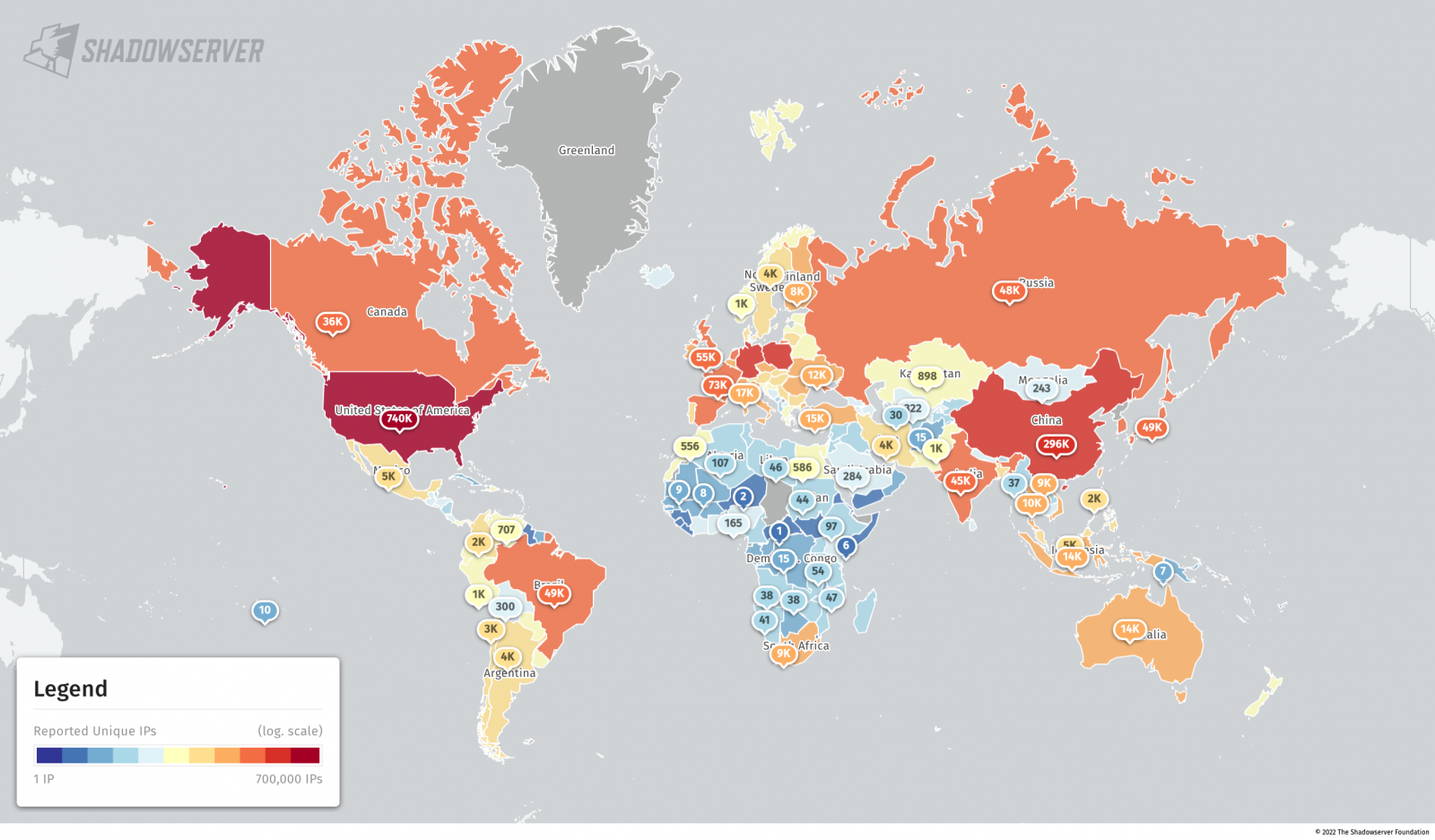
The scan results in detail are the following:
- Total exposed population on IPv4: 3,957,457
- Total exposed population on IPv6: 1,421,010
- Total "Server Greeting" responses on IPv4: 2,279,908
- Total "Server Greeting" responses on IPv6: 1,343,993
- 67% of all MySQL services found are accessible from the internet
To learn how to securely deploy MySQL servers and close the security gaps that might lurk in your systems, Shadow Server recommends admins read this guide for version 5.7 or this one for version 8.0.
Data brokers who sell stolen databases have told BleepingComputer that one of the most common vectors for data theft is improperly secured databases, which admin should always lockdown to prevent unauthorized remote access.
Failing to secure MySQL database servers can result in catastrophic data breaches, destructive attacks, ransom demands, remote access trojan (RAT) infections, or even Cobalt Strike compromises.
These scenarios all have severe consequences for the impacted organizations, so it is crucial to apply the appropriate security practices and remove your devices from being accessible on simple network scans.
Break down IAM silos like Bitpanda, KnowBe4, and PathAI
Broken IAM isn't just an IT problem - the impact ripples across your whole business.
This practical guide covers why traditional IAM practices fail to keep up with modern demands, examples of what "good" IAM looks like, and a simple checklist for building a scalable strategy.








Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now